Unauthenticated Scanning.
Overview
What is Unauthenticated API Scanning?
Unauthenticated scanning refers to the process of testing API endpoints without providing authentication credentials such as API keys, OAuth tokens, or session-based authentication. This allows security teams to evaluate how an API behaves when accessed without valid authentication and identify potential security risks that may exist before authentication is enforced.
APIs often expose public-facing endpoints that are meant to be accessed without authentication (e.g., status checks, public data feeds) or endpoints that unintentionally allow unauthenticated access due to misconfigurations. Unauthenticated scanning helps detect these issues early, reducing the risk of unauthorized access, data leaks, and API abuse.
Why Perform an Unauthenticated Scan?
Scanning API endpoints without authentication is an essential security practice for multiple reasons:
- Identifies Publicly Accessible Endpoints
- Ensures that only intended endpoints are accessible without authentication.
- Detects any API endpoints that are unintentionally left unprotected.
- Validates API Access Controls
- Confirms that restricted endpoints correctly enforce authentication.
- Detects misconfigurations where authentication is missing or bypassable.
- Exposes Security Weaknesses in Public APIs
- Identifies unauthenticated endpoints that may leak sensitive data.
- Detects API rate limiting issues where unrestricted access could lead to API abuse.
- Complements Authenticated API Scanning
- Helps differentiate between authentication failures and endpoint-specific vulnerabilities.
- Ensures a layered security approach by evaluating APIs both before and after authentication is enforced.
Common Issues Detected in Unauthenticated API Scanning
Unauthenticated API scans frequently uncover security misconfigurations, including:
- Unprotected Endpoints: APIs that should require authentication but allow unauthenticated access.
- Sensitive Data Exposure: Publicly accessible API responses containing user data, credentials, or internal system details.
- Improperly Configured Authorization Controls: Endpoints that allow actions (e.g., data modification) without authentication.
- Lack of Rate Limiting: APIs that do not restrict request frequency, making them vulnerable to abuse or denial-of-service attacks.
- Overly Permissive CORS Policies: APIs that allow unauthenticated cross-origin requests, increasing the risk of data leakage.
When to Perform an Unauthenticated Scan?
Unauthenticated API scans should be performed:
- Before deploying an API to production to validate that authentication is correctly enforced.
- As part of routine security testing to ensure access controls are not inadvertently bypassed.
- When onboarding a third-party API to assess its exposure before integration.
- After updates or configuration changes to verify that authentication mechanisms remain intact.
- In response to security incidents where unauthorized access attempts have been detected.
How Unauthenticated Scanning Fits into API Security Strategy
Unauthenticated scanning plays a critical role in proactive API security by:
- Identifying endpoints that should be restricted but are publicly accessible.
- Verifying that authentication mechanisms are properly implemented.
- Providing insights on how an API behaves when accessed without credentials.
- To strengthen API security, unauthenticated scanning should be complemented with:
- Authenticated API Scanning: To evaluate security risks after authentication is provided.
- Runtime Security Monitoring: To detect unauthorized access attempts in real-time.
- Security Testing in CI/CD Pipelines: To automate scans before production deployment.
By incorporating unauthenticated scanning into API security practices, teams can identify and mitigate potential security gaps before they can be exploited.
Next Steps
The following section will provide a step-by-step guide on how to:
- Initiate an unauthenticated API scan
- Define and adjust the scan scope
- Execute the scan and track its progress
- Analyze scan results and take corrective actions
By following these steps, security teams can ensure that their APIs are properly protected and enforce authentication as intended.
Navigate to URL
Open your browser and visit: https://<your-tenant>.apisecapps.com
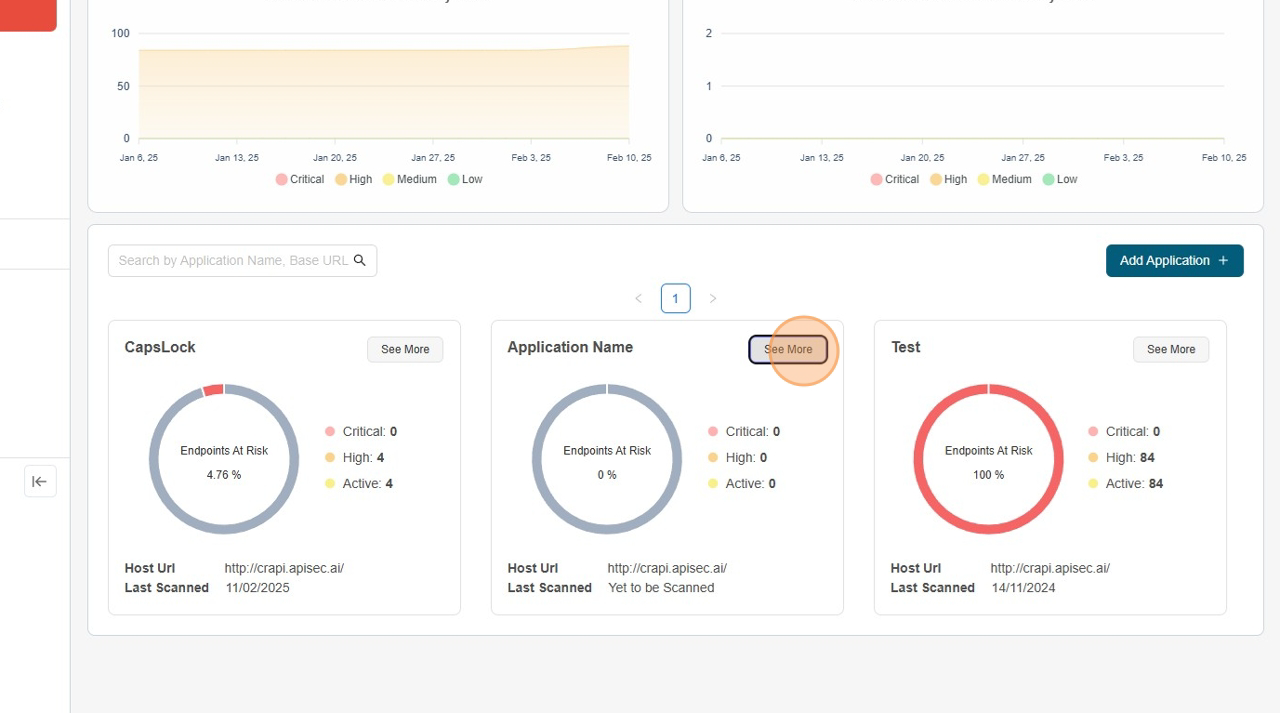
Visit the application
- Click on "See more" to open the application
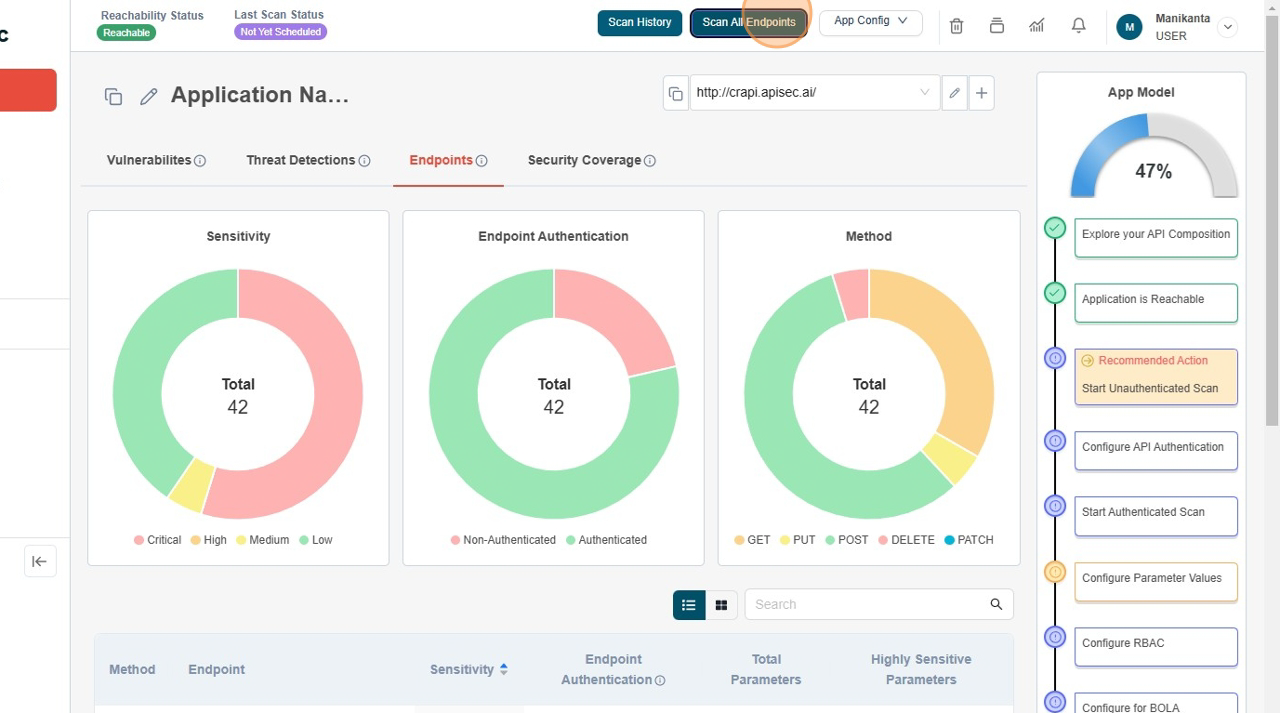
Initiating unauthenticated scan
- Click "Scan All Endpoints"
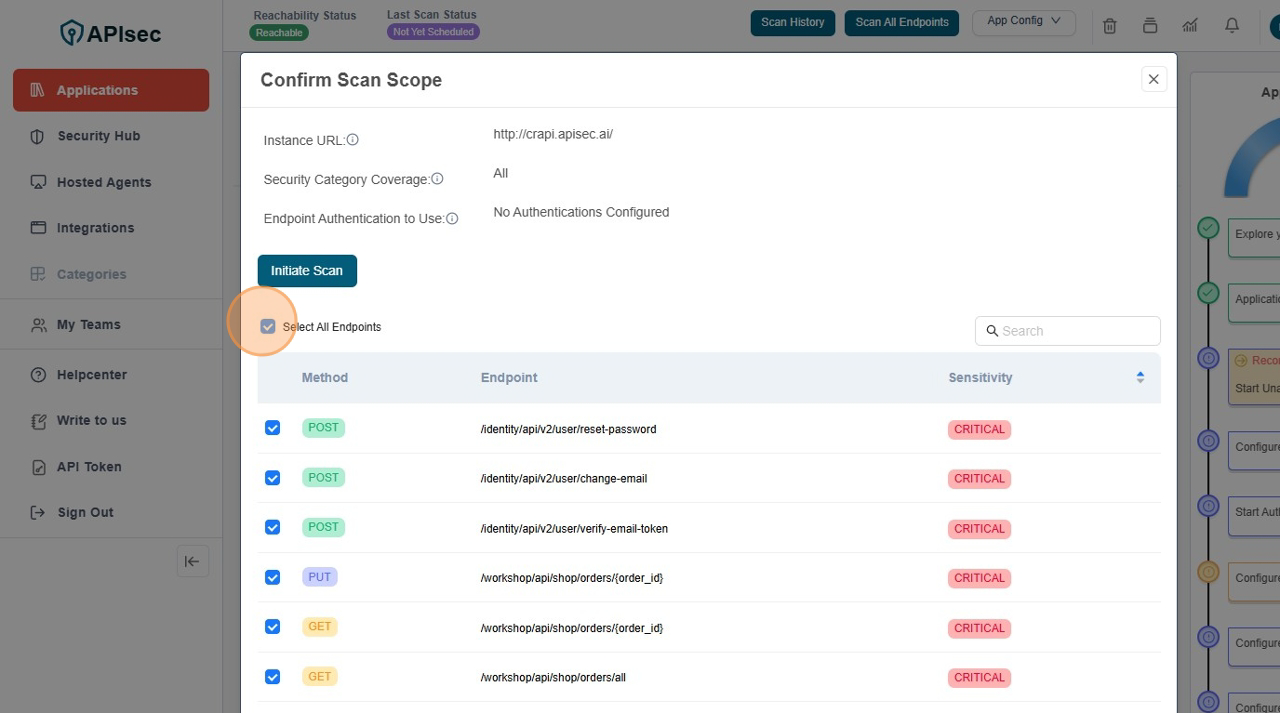
Confirm the Scan Scope
Here you can customize your scan, like search "Orders" api and then initiate the scan.
-
Unselect all endpoints, Click the "Select All Endpoints" field to remove all selection of API's
-
Type "Orders" in Search field.
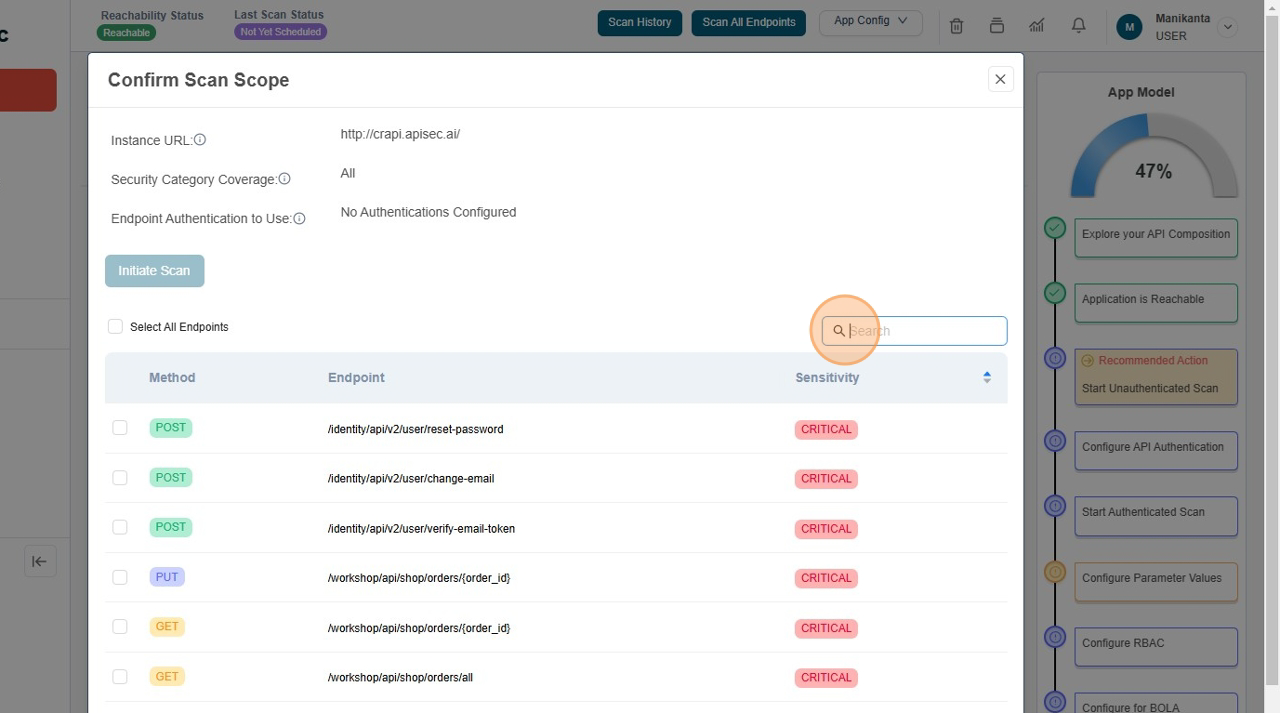
-
Click the "Select All Endpoints" field; to select the all Orders related API's
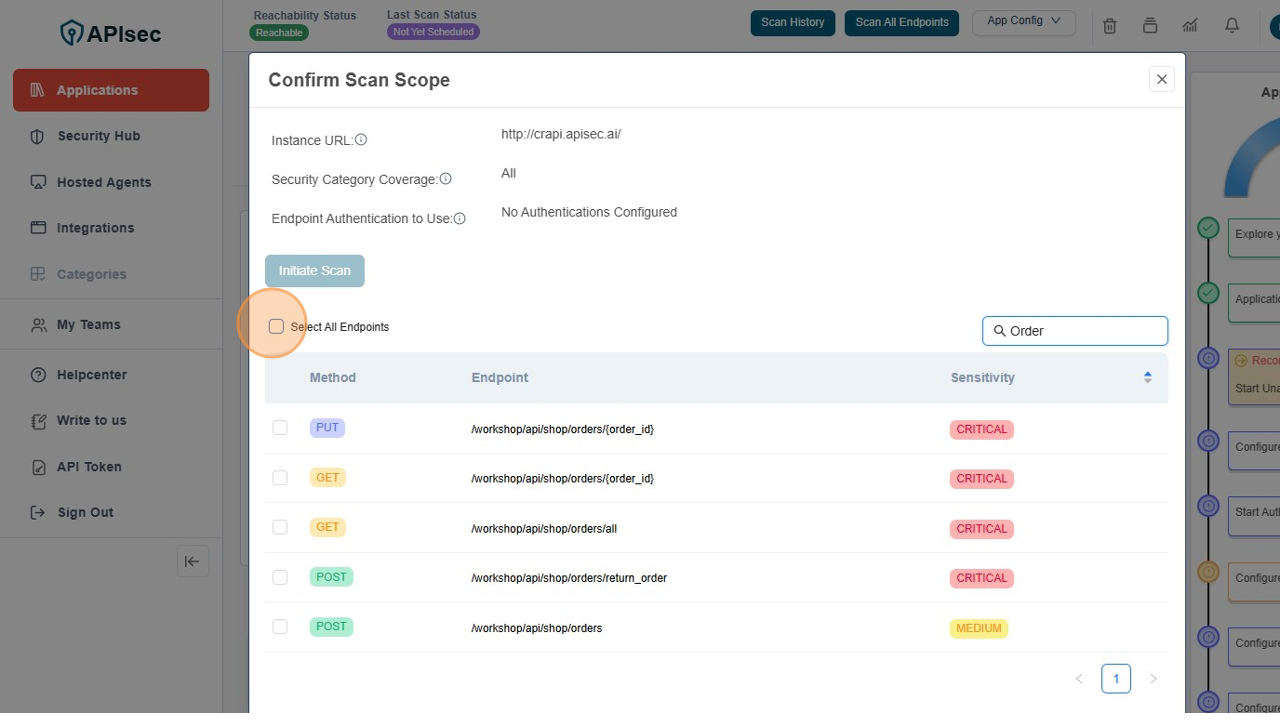
-
Check the No Authentication Configured under the head of Endpoint Authentication to use
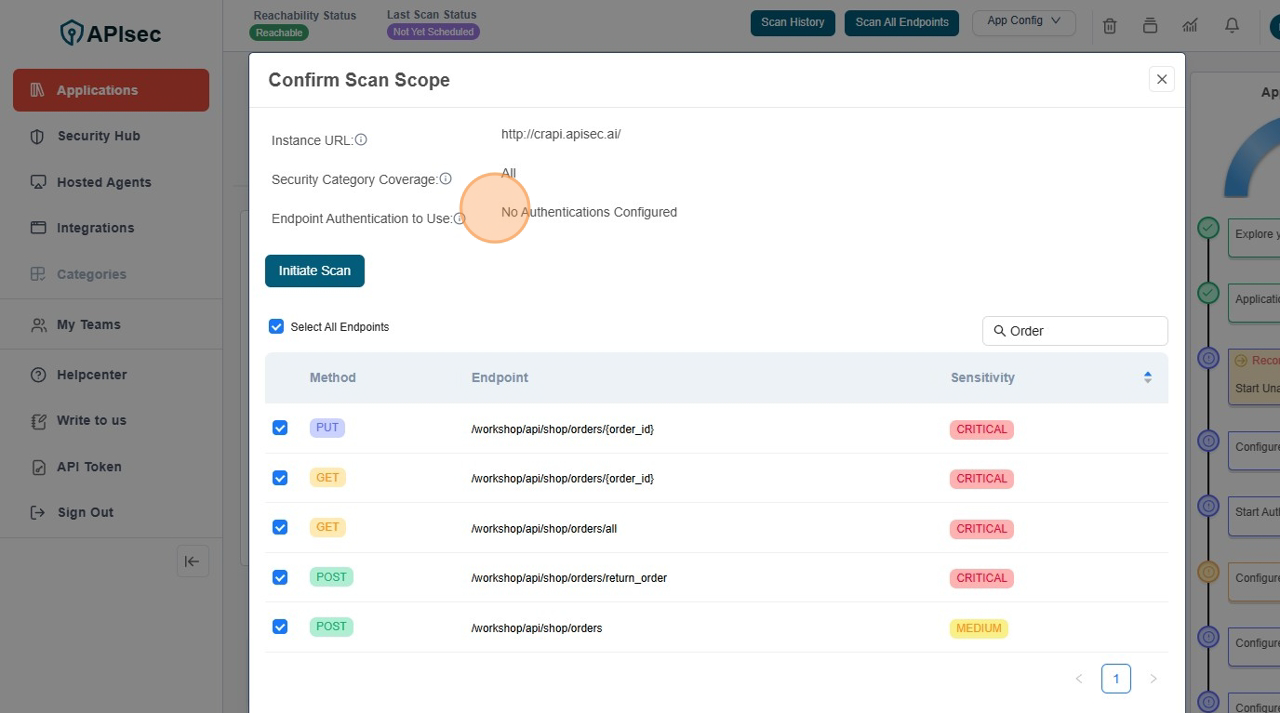
-
Click on Initiate Scan
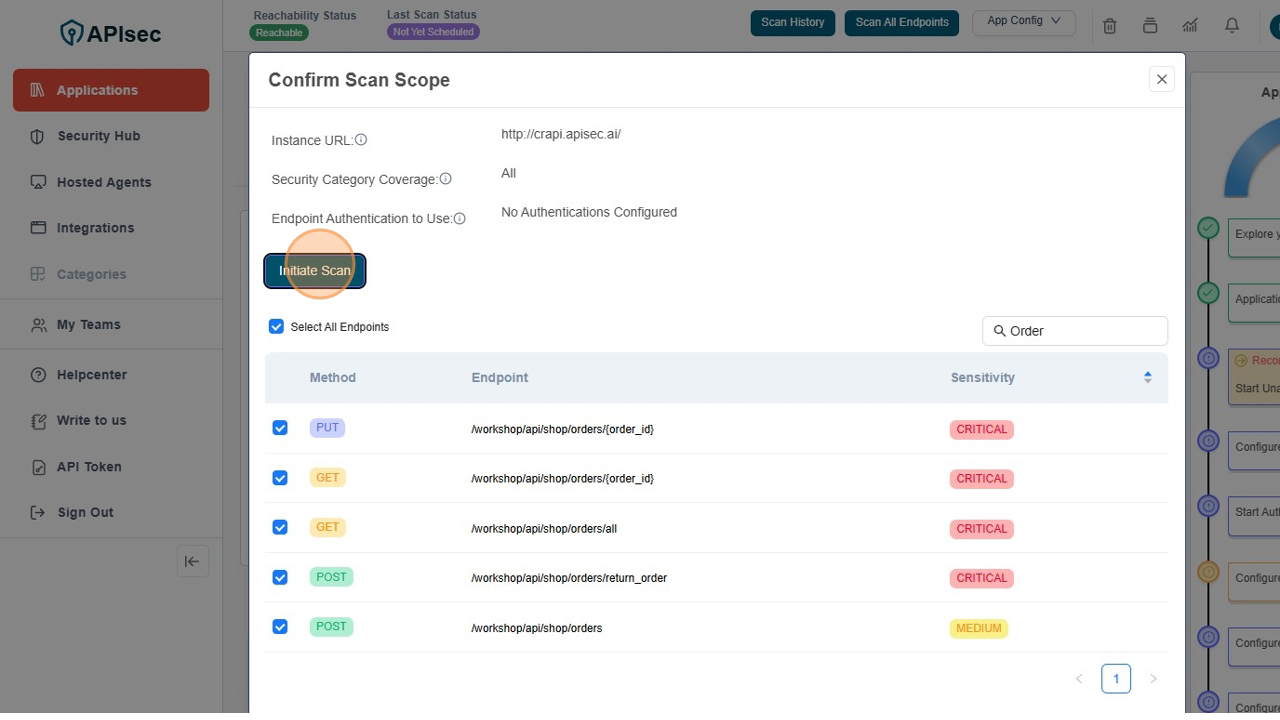
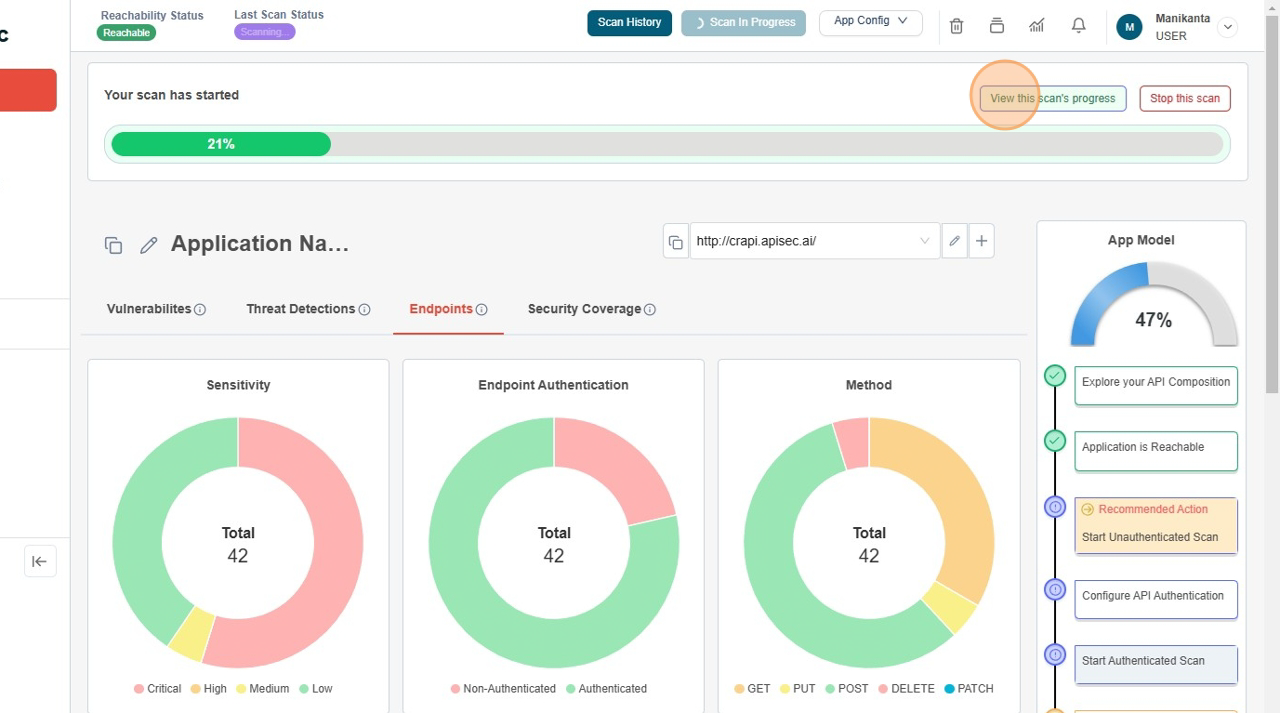
Confirm the Scan has started
- You can scan progress bar in top of the Application Name
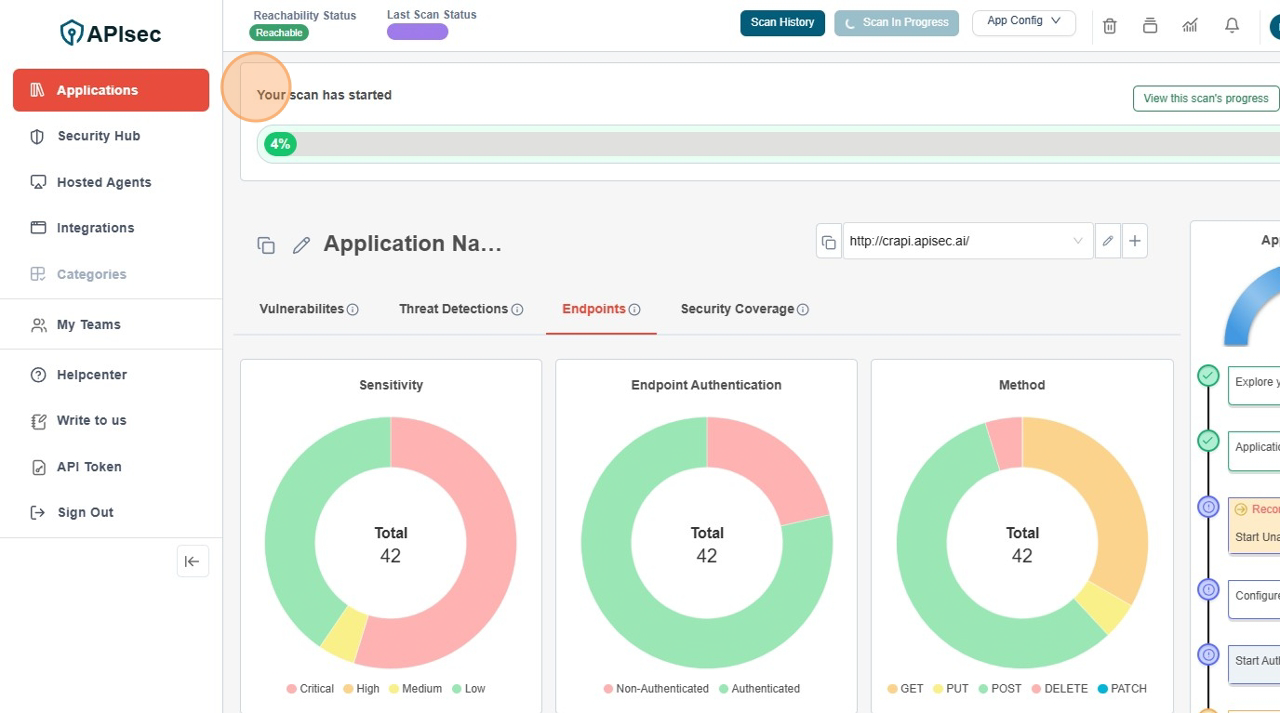
Scan Details Page with current scan's progress
Click "View this scan's progress"